Oncotarget Volume 11, Issue 35 published "Targeting 14-3-3ε-CDC25A interactions to trigger apoptotic cell death in skin cancer" by Holmes et, al. which reported that the authors previously documented an anti-apoptotic role for CDC25A in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, an activity dependent on its association with 14-3-3 proteins.
The authors hypothesized that targeting CDC25A-14-3-3ε interactions may be an effective strategy for inducing skin cancer cell apoptosis.
Co-immunoprecipitation revealed that CDC25A associated with 14-3-3ε, 14-3-3γ and 14-3-3ζ in SCC cells but not normal keratinocytes.
14-3-3ε and CDC25A activated Akt/BAD/Survivin pro-survival signaling. To target the interaction of 14-3-3ε with CDC25A for cancer therapy, they developed two novel phospho-peptides, pS and pT, corresponding to each of the 14-3-3 binding sites of CDC25A, to specifically interfere with 14-3-3ε binding to CDC25A.
Peptides pT, and pS induced SCC cell death and blocked 14-3-3ε binding to CDC25A.
Dr. Sándor Lovas and Dr. Laura A. Hansen from The Creighton University School of Medicine, Department of Biomedical Sciences in Omaha, Nebraska said, "Skin cancer is the most common malignancy in humans, with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) representing 20% of cases."
In cutaneous SCC the Oncotarget authors showed that, similar to CDC25A, 14-3-3ε is enriched in the cytoplasm of SCC cells where it inhibits apoptosis through promotion of Akt/BAD/Survivin pro-survival signaling. Association of CDC25A with 14-3-3ε inhibits the ability of CDC25A to promote cell cycle progression in neuronal and HeLa cells.
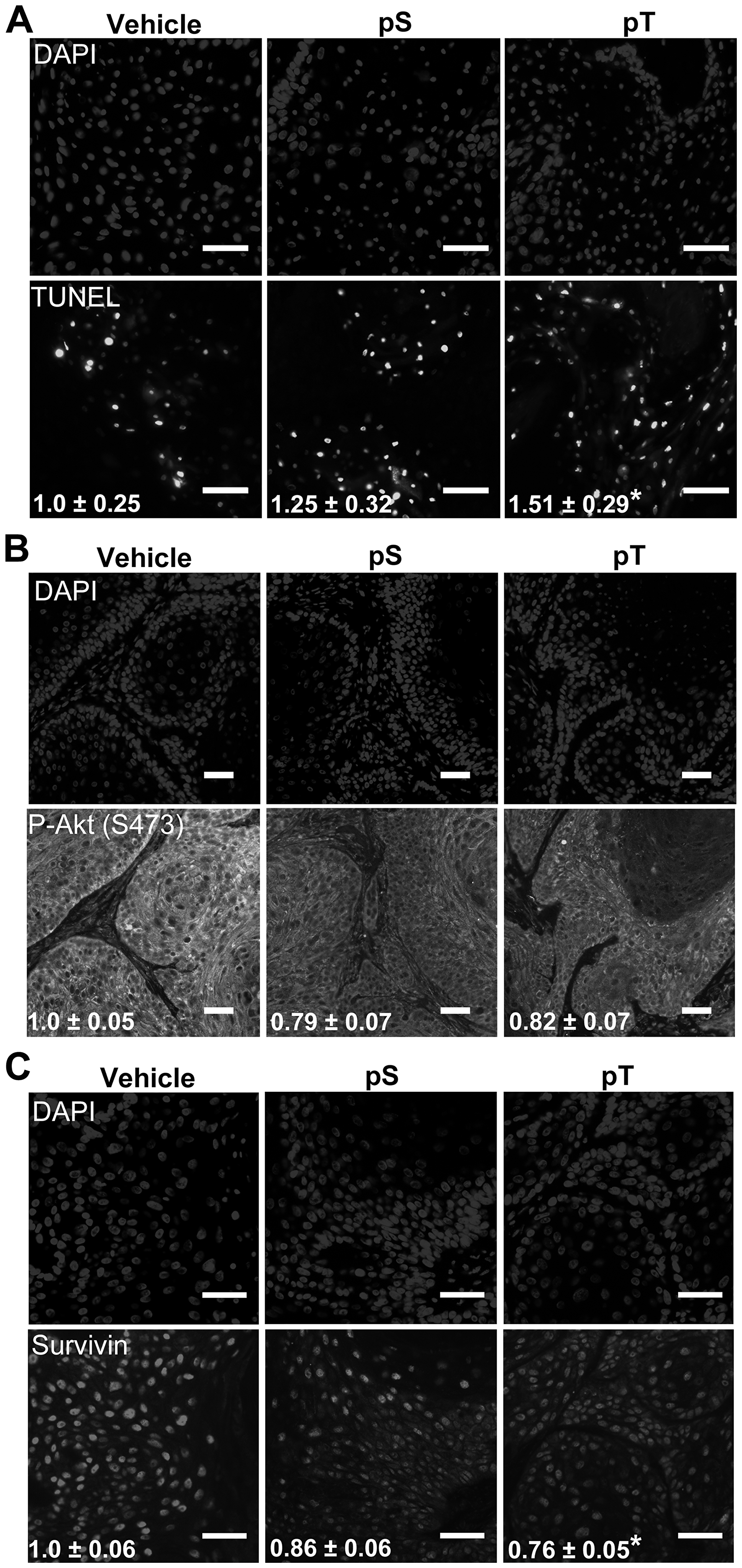
Figure 5: Targeting 14-3-3ε-CDC25A binding increases apoptosis in vivo (A) TUNEL labeling to detect apoptotic nuclei (bottom) was performed on whole tumor sections from vehicle, pS or pT-treated mouse xenografts with DAPI-labeled nuclei (top) (scale bar = 50 μm); the average number of apoptotic cells per μm2 ± SEM, indicated in white font, were obtained by counting TUNEL positive cells on whole tumor sections using Olympus VS120 analysis software and normalizing to the area of the tumor section; images are representative of tumors from 3 mice (N = 3). (B, C) Immunofluorescence for P-Akt (S473) (B) or Survivin (C) (bottom) was performed on whole tumor sections from vehicle, pS or pT (N = 3) treated tumors with DAPI identification of nuclei (top) (Scale bar = 50 μm); white font indicates the average FITC intensity ± SEM of the whole tumor section from each mouse (N = 3). Significance determined using a two-tailed Student's t-test, P ≤ 0.05.
Specifically, in neuronal cells, release of CDC25A from 14-3-3ε binding increases the phosphatase activity of CDC25A and increases neuronal cell death.
However, whether 14-3-3ε associates with CDC25A in skin cancer cells, and what effect targeting this interaction may have on SCC cell viability has not been previously reported.
CDC25A and 14-3-3ε similarly activated a Akt/BAD/Survivin pro-survival signaling pathway in SCC cells and suppressed cell death.
"CDC25A and 14-3-3ε similarly activated a Akt/BAD/Survivin pro-survival signaling pathway in SCC cells and suppressed cell death."
The authors characterized two phospho-peptide fragments of CDC25A phospho-Ser178 and phospho-Thr507, which are part of the region of CDC25A's 14-3-3ε binding sites, in order to disrupt 14-3-3ε-CDC25A binding. Both peptides reduced 14-3-3ε and CDC25A interactions in SCC cells and also increased apoptosis.
The Lovas/Hansen Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Paper that we have demonstrated that CDC25A associated with 14-3-3ε, 14-3-3γ and 14-3-3ζ in SCC cells.
CDC25A and 14-3-3ε inhibited apoptosis by promoting the activation of Akt, inhibition of BAD and an increase in Survivin, the same pathway that we have shown to be regulated by 14-3-3ε.
Also, to the best of their knowledge, this is the first time that P-CDC25A and P-CDC25A peptide fragments have been shown to directly interact with 14-3-3ε in a cellular environment.
Treatment of SCC cells with the peptide fragments reduced the interaction of 14-3-3ε with CDC25A, decreased SCC cell viability and increased apoptosis both in vitro and in vivo.
In all, they have demonstrated the potential of blocking CDC25A binding to 14-3-3ε in targeting skin cancer cells.
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.27700
Full text - https://www.oncotarget.com/article/27700/text/
Correspondence to - Sándor Lovas - [email protected] and Laura A. Hansen - [email protected]
Keywords - skin cancer, squamous cell carcinoma, CDC25A, 14-3-3ε, apoptosis
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a biweekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https://www.oncotarget.com or connect with:
SoundCloud - https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/oncotarget
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
Reddit - https://www.reddit.com/user/Oncotarget/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit http://www.ImpactJournals.com or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
[email protected]
18009220957x105





