Corrections:
Correction: H2O2 treatment or serum deprivation induces autophagy and apoptosis in naked mole-rat skin fibroblasts by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
Metrics: PDF 2254 views | ?
Present: The images displayed in Figure 4 are incorrect.
Corrected: The proper figure 4 appears below.
Original article: Oncotarget. 2016; 7:84839-50. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13321.
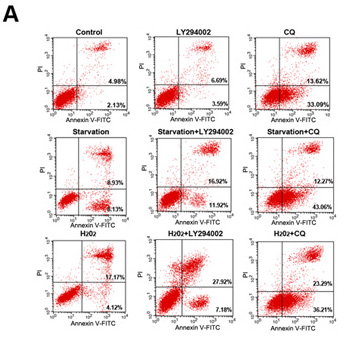


Figure 4: LY294002-induced inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling increases apoptosis in skin fibroblasts. (A) Flow cytometric analysis revealed that 12 h of treatment with LY294002 or CQ increased early and late apoptosis rates, and further increased starvation- or H2O2 treatment-induced increases in apoptosis rates, in skin fibroblasts. (B) Bar graph showing early and late apoptotic cell percentages. Means ± standard error are shown. (C–J) Western blots revealed that Bax levels increased, while Bcl2, p70S6K, p53, HIF1-α, and caspase-3 levels decreased, following 12 h of serum starvation or H2O2 treatment with or without LY294002 or CQ. Bar graphs show mean relative protein levels normalized to β-actin.
 All site content, except where otherwise noted, is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
All site content, except where otherwise noted, is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
PII: 18611
